Content
- ES6 (ECMAScript 2015)
- ES7 (ECMAScript 2016)
- ES8 (ECMAScript 2017)
- ES9 (ECMAScript 2018)
- ES10 (ECMAScript 2019)
- ES11 (ECMAScript 2020)
- ES12 (ECMAScript 2021)
ES6 (ECMAScript 2015)
1. let/const
let
以前在宣告變數都使用全域的var在 ES6 新增了let可以更明確的規範變數作用的範圍。
function f() {
let x = 1;
{
console.log(x); // 1
let y = 2;
}
console.log(y); // Uncaught ReferenceError: y is not defined
}
f();
const 簡化了定義常數的宣告,常數必須初始化且不能變更。
const PI = 3.14;
2. arrow functions
var a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
//ES5
a.map(function (v) {
return v + 1;
});
//ES6
a.map((v) => v + 1);
3. classes
加入 classes,定義 class 更直觀。在 ES5 以前定義物件很複雜,沒有 class 關鍵字,所以會看到很多XXX.prototype.YYY的語法,在 ES6 幾乎看不見,精簡許多。
- ES6 建立 Stack Class
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.stack = [];
}
push(num) {
this.stack.push(num);
}
pop() {
return this.stack.pop();
}
size() {
return this.stack.length;
}
}
s = new Stack();
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.pop(); // 3
s.size(); // 2
- ES6 之前的寫法
const Stack = function () {
this.stack = [];
};
Stack.prototype.push = function (num) {
this.stack.push(num);
};
Stack.prototype.pop = function () {
return this.stack.pop();
};
Stack.prototype.size = function () {
return this.stack.length;
};
- 繼承寫法
class Animal {
constructor(name, leg) {
this.name = name;
this.leg = leg;
}
bark() {
console.log("animal bark");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
constructor({ name, leg }) {
super(name, leg);
this.run = true;
this.fly = false;
}
bark() {
console.log("meow");
}
}
let cat = new Cat({ name: "Jack", leg: 4 });
cat; // Cat {name: "Jack", leg: 4, run: true, fly: false}
cat.bark(); // meow
4. template string
允許在字串中插入變數,不用像以前一樣做字串串接。
let name = "Tom";
let template = `Hello, ${name}.`; // "Hello, Tom."
5. destructuring
在拆解陣列或是物件時更方便
let num = [1, 2, 3];
let [a, b, c] = num; // a = 1, b = 2, c = 3
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
let { a, b, c } = obj;
console.log(a, b, c); // 1, 2, 3
6. default + rest + speard
-
default
在傳遞參數允許設定預設值,能夠預防一些例外產生 e.g.
let f = (a = 1, b = 2, c = 3) => {
console.log(a, b, c);
};
f(); // 1 2 3
f(4, 5); // 4 5 3
f(4, 5, 6); // 4 5 6
-
rest
在使用函數或是設計函數上可能會遇上不確定到底要幾個參數, ES6 可以讓你在這方面更有彈性。不確定的參數使用
...p作表示,p 為一個陣列。
let f = (a, ...rest) => {
console.log(a, rest);
};
f(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 1 [2, 3, 4, 5]
- spread
let arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
let arr2 = [4, 5, 6];
let arr3 = [...arr1, ...arr2]; // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
7. iterators + for..of
let nums = [1, 2, 3, 4];
for (let n of nums) {
console.log(n);
}
/*
1
2
3
4
*/
8. Generators
- 一般 function
function f() {
console.log("1.");
console.log("2.");
return "Hello World";
}
- generator function
會在 function 保留字後面在加上星號(*)
generator function 回傳值是 generator object, 是一個 iterator
genertaor function 內使用yield來暫停執行。
function* f() {
yield "yield 1.";
console.log("1.");
yield "yield 2.";
console.log("2.");
return "Hello World";
}
const iter = f();
iter.next(); // {value: 'yield 1.', done: false}
iter.next(); // {value: 'yield 2.', done: false}
iter.next(); // {value: 'Hello World', done: true}
function* f() {
yield "a";
yield "b";
yield "c";
yield "d";
}
const iter = f();
console.log([...iter]); // [a, b, c, d]
費式數列例子
// Generates an infinite stream of Fibonacci numbers.
// The generator doesn't keep the array of all numbers.
function* fibonacci(): IterableIterator<number> {
let [a, b] = [0, 1];
while (true) {
yield a;
[a, b] = [b, a + b];
}
}
function print(n: number) {
let i = 0;
for (const fib of fibonacci()) {
if (i++ === n) break;
console.log(fib);
}
}
// Print first 10 Fibonacci numbers.
print(10);
- Reference
在遇到 generator.return()時會直接返回{done: true}
function* print(i){
let index = 0
while(true){
yield index++
}
}
g = print(0)
g.next() // {value: 0, done: false}
g.next() // {value: 1, done: false}
g.return() // {value: undefined, done: true}
g.next() // {value: undefined, done: true}
9. unicode
s = "\u{1F602}"; //"😂"
10. modules
// a.js
const a = () => {
console.log("a.js");
};
module.exports = a;
// b.js
import a from "./a";
a(); // a.js
11. map/set/weakmap/weakset
-
map / weakmap
Map 的 key 值可以是任意型態(int, string, array)
WeakMap 的 key 值只能是物件
let map = new Map();
map.set(1, "1");
map.set("a", "a");
map.set(["arr1"], ["arr2"]);
map; // {1 => "1", "a" => "a", ["arr1"] => ["arr2"]}
let weakmap = new WeakMap();
weakmap.set(1, "1");
// Uncaught TypeError: Invalid value used as weak map key
weakmap.set("a", "a");
// Uncaught TypeError: Invalid value used as weak map key
weakmap.set(["arr1"], ["arr2"]); // {["arr1"] => ["arr2"]}
- set / weakset
Set 與 WeakSet 差異: Set 能夠儲存隨意型態(int, string, array), WeakSet 只能夠儲存物件。
let set = new Set();
set.add(1).add(2).add(5); // {1, 2, 5}
set.add(2); // {1, 2, 5}
set.add("2"); // // {1, 2, 5, "2"}
set.add([1, 2, 3]); // {1, 2, 5, "2", [1,2,3]}
set.size; // 5
let weakset = new WeakSet();
weakset.add(1);
// Uncaught TypeError: Invalid value used in weak set
weakset.add([1, 2, 3]); // {[1,2,3]}
weakset.add([1, 2, 3]); // {[1,2,3], [1,2,3]}
12. proxying/refection
13. symbols
symbol 是 ES6 新增的一種基本數據型態(primitive data type)。
基本型態有七種: string,number,bigint,boolean,null,undefined,symbol。
特性: 唯一且不可改變(immutable)的資料型態,可用來識別物件的屬性。
let a = Symbol("123");
let b = Symbol("123");
a === b; // false
let a = Symbol("aaa");
let b = Symbol("bbb");
let obj = { [a]: 123, [b]: 456 };
obj; // {Symbol(aaa): 123, Symbol(bbb): 456}
14. promises
程式常常需要做 request 到後端來取得資料,但 server 並不會馬上回傳資料,要等待 server 處理的時間。這時程式就必須停下來等待,造成時間浪費。
ES6 提出了 promise 來解決這個非同步(asynchronously)的狀況。當發送 request 到 server 後,並不會停下來等 server 處理完,而是留下 callback 後,繼續執行後面任務。
當 server 成功處理好拿到資料準備回傳時,再去執行剛剛留下的 callback function。留下的 callback function 有分為 request 呼叫成功(resolve)與 request 呼叫失敗(reject)。
const callServer = (time) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (time <= 300) {
setTimeout(() => resolve({ msg: "request success!" }), time);
} else {
setTimeout(() => reject({ msg: "request failed!" }), time);
}
});
};
callServer(200).then((res) => console.log(res));
// {msg: "request success!"}
callServer(400)
.then((res) => console.log(res))
.catch((e) => console.log(e)); // <--
// {msg: "request failed!"}
15. binary and octal literals
支援二進位與八進位表示
0b111; //7
0o123; //83
let num = "1010";
let binNum = `0b${num}`;
let decNum = BigInt(binNum); // 10n
decNum.toString(2); // "1010"
ES7 (ECMAScript 2016)
1. Exponentiation Operator
2 ** 3; // 8
2. Array.includes()
let arr = ["Tom", "Jack", "David"];
arr.includes("Tom"); // true
ES8 (ECMAScript 2017)
1. Async functions (MDN)
可以用來簡化 ES6 Promise 寫法,await 表達式只能在 async 函式內部使用,await 會等待 Promise 解析完畢才會繼續往下執行。
之前 ES6 Promise 範例,在 callServer()之後要處理回傳的 Promise 需要使用.then()來接。若拿回來的資料還要當做其他 function 的 input 會遇到.then().then().then()的狀況。
const callServer = (time) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (time <= 300) {
setTimeout(() => resolve({ msg: "request success!" }), time);
} else {
setTimeout(() => reject({ msg: "request failed!" }), time);
}
});
};
callServer(200).then((res) => console.log(res));
// {msg: "request success!"}
callServer(400)
.then((res) => console.log(res))
.catch((e) => console.log(e)); // <--
// {msg: "request failed!"}
ES8 async function 可以改善處理 promise 的寫法。
const callServer = (time) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (time <= 300) {
setTimeout(() => resolve({ msg: "request success!" }), time);
} else {
setTimeout(() => reject({ msg: "request failed!" }), time);
}
});
};
const run = async () => {
let success = await callServer(200);
let error = {};
try {
error = await callServer(400);
} catch (err) {
error = err;
}
console.log(success); // {msg: "request success!"}
console.log(error); // {msg: "request failed!"}
};
run();
2. Object.entries
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
for (let [key, value] of Object.entries(obj)) {
console.log(key, value);
}
/*
a 1
b 2
c 3
*/
3. Object.values
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
for (let value of Object.values(obj)) {
console.log(value);
}
/*
1
2
3
*/
4. Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
let descriptors = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj);
descriptors;
/*
{
a: {value: 1, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
b: {value: 2, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
c: {value: 3, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
}
*/
5. String.padStart() (MDN), String.padEnd() (MDN)
-
String.padStart()
str.padStart(targetLength [, padString])
"101".padStart(8); // " 101"
"101".padStart(8, "0"); // "00000101"
"101".padStart(8, "xyz"); // "xyzxy101"
- String.padEnd()
"101".padEnd(8); // "101 "
"101".padEnd(8, "0"); // "10100000"
"101".padEnd(8, "xyz"); // "101xyzxy"
6. Shared memory and Atomic
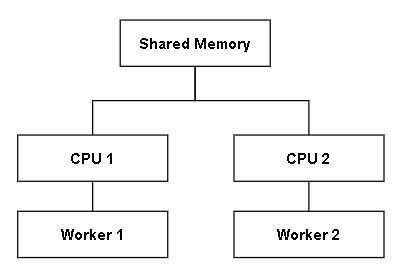
Atomic 是類似鎖,當 CPU1 在讀寫 shared memory 時,會把 shared memory 中的值複製一份到 cache 中。在讀寫時把 shared memory 鎖住,讓其他 CPU 不能夠讀寫,避免複製到舊的值,確保資料一致性。
ES9 (ECMAScript 2018)
1. Object rest and spread
在 ES6 加入的 rest 與 spread 只能針對陣列做展開,ES8 擴展到也能夠針對物件展開。
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
let { a, ...rest } = obj;
a; // 1
rest; // {b: 2, c: 3}
2. Promise.finally
不管 Promise 是 resolve 還是 reject 都會執行 finally(),可以用來關閉 loading 狀態。
const fetchData = (time) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (time <= 300) {
setTimeout(() => resolve({ data: "request success" }), time);
} else {
setTimeout(() => reject({ data: "request failed!" }), time);
}
});
};
const run = async () => {
fetchData(400)
.then(({ data }) => console.log(data))
.catch((err) => console.log(err))
.finally(() => console.log("finally"));
};
run();
// {data: "request failed!"}
// finally
3. Asynchronous Iteration
支援在 for 迴圈內呼叫非同步 function。
const fetchData = (time) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(`success: ${time}ms`), time);
});
};
const run = async () => {
let times = [500, 1000, 2000];
for await (let ms of times) {
fetchData(ms).then((res) => console.log(res));
}
};
run();
// success: 500ms
// success: 1000ms
// success: 2000ms
4. Regular Expression Features
- Named capture groups
在正規表達式內使用?<name>來幫 group 取名字
const re = /(?<year>[0-9]{4})-(?<month>[0-9]{2})-(?<day>[0-9]{2})/;
const match = re.exec("2021-09-05");
match.groups; // {year: "2021", month: "09", day: "05"}
-
dotAll
tc39/proposal-regexp-dotall-flag.在正規表達式中代表任意字元,但不能是換行符號(line terminator)/foo.bar/.test("fooAbar") // true /foo.bar/.test("foo\nbar") // false建議解決方案
增加 s flag,讓.能夠匹配任何字元包含換行符號/foo.bar/s.test("foo\nbar") // true -
lookbehind assertions
tc39/proposal-regexp-lookbehind- Positive
(?<=...)
(?<=x)y表示 x 後面接著 y,才會匹配 ylet re = /(?<=\$)\d+\.\d+/; re.exec("$10.53"); // ["10.53", index: 1, input: "$10.53", groups: undefined] re.exec("€10.53"); // null - Negative
(?<!...)
(?<!x)y表示 x 後面不是 y,才會匹配 y
- Positive
-
Unicode property escapes
tc39/proposal-regexp-unicode-property-escapesconst regexGreekSymbol = /\p{Script=Greek}/u; regexGreekSymbol.test("π"); // true
5. Escape sequences allowed in tagged template literals
const tagged = (s, version, year) => {
console.log(s);
console.log(version);
console.log(year);
};
let version = "ES9";
let year = 2018;
console.log(tagged`This is ${version} (ECMAScript${year}).`);
/*
["This is ", " (ECMAScript", ").", raw: Array(3)]
ES9
2018
*/
ES10 (ECMAScript 2019)
1. Array.flat() (MDN) / Array.flatMap() (MDN)
- flat(deep)
let arr1 = [1, 2, [3, 4]];
arr1.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
let arr2 = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6]]];
arr2.flat(); // [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6]]
arr2.flat(2); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
let arr3 = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6, [7, 8, [9, 10]]]]];
arr3.flat(Infinity); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
- flatMap()
和 map()差在 map()完會再經過一層的 flat()展開。
2. Object.fromEntries()(MDN)
把 Map、Array 傳換成物件。
const map = new Map([
["a", 1],
["b", 2],
]);
map; // Map(2) {'a' => 1, 'b' => 2}
Object.fromEntries(map); // {a: 1, b: 2}
let arr = [
["a", 1],
["b", 2],
["c", 3],
];
Object.fromEntries(arr); // {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}
3. String.trimStart() / String.trimEnd()
去除左邊/右邊空白並返回一個新的字串,不會直接修改原來的值。
let s = " hello ";
s.trimStart(); // 'hello '
s.trimEnd(); // ' hello'
ES11 (ECMAScript 2020)
1. string.matchAll() (MDN)
let s = "abcdacd";
console.log([...s.matchAll(/a/g)]);
/*
[
['a', index: 0, input: 'abcdacd', groups: undefined],
['a', index: 4, input: 'abcdacd', groups: undefined]
]
*/
2. BigInt
遇到類似Leetcode 1985這類問題, Number 型態已經不足夠表示。Number 型態表示上限為。
Math.pow(2, 53); // 9007199254740992
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; // 9007199254740991
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 1; // 9007199254740992
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 2; // 9007199254740992
BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) + BigInt(1); // 9007199254740992n
BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) + BigInt(2); // 9007199254740993n
3. Promise.allSettled
Promise.all() 在遇到 reject 時會停止後續動作(short-circuit),直接噴錯。
Promise.allSettled() 其中有遇到 reject 還是會將其他 promise 執行完畢。
let promise1 = Promise.resolve(3);
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(reject("error"));
});
let promise3 = 42;
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3])
.then((values) => {
console.log(values);
})
.catch(() => console.log("error"));
// error
Promise.allSettled([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then((values) => {
console.log(values);
});
/*
[
{ status: 'fulfilled', value: 3 },
{ status: 'rejected', reason: 'error' },
{ status: 'fulfilled', value: 42 }
]
*/
4. globalThis
var a = 10 // Window{..., a: 10, ...}
(function () {
let a = 20
console.log(a) // 20
console.log(this.a) // 10
console.log(window.a) // 10
console.log(frames.a) // 10
console.log(globalThis.a) // 10
})()
5. Nullish coalescing Operator (??) (MDN)
??左側為否定只判斷null和undefined
console.log(null ?? "hello"); // hello
console.log(undefined ?? "hello"); // hello
console.log(false ?? "hello"); // false
console.log(0 ?? "hello"); // 0
console.log("" ?? "hello"); // ""
console.log(null || "hello"); // hello
console.log(undefined || "hello"); // hello
console.log(false || "hello"); // hello
console.log(0 || "hello"); // hello
console.log("" || "hello"); // hello
6. Optional Chaining (?.)
let a = {
b: {
c: 1,
},
};
a.b.c; // 1
a.d.c; // TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined
a?.d?.c; // undefined
7. module
import()
支援動態載入,可在需要時才 import。import.metaexport \* as ns from 'module'
ES12 (ECMAScript 2021)
1. replaceAll
let str = "ABCDFABCGHIABC";
str.replaceAll("ABC", "xxx"); // 'xxxDFxxxGHIxxx'
str.replace(/ABC/g, "xxx"); // 'xxxDFxxxGHIxxx'
2. Promise.any
a Promise combinator that short-circuits when an input value is fulfilled (遇到的第一個 Promise 是 fullilled 就回傳,後面的都不做了)
-
Promise.all
所有的 Promise 都要 fulfilled 否則報錯
-
Promise.allSettled
遇到 Promise 是 rejected 還是會把後面的 Promise 做完
-
Promise.any
會傳第一個 fulfilled 的 Promise,之後的 Promise 不執行。
若全部都是 rejected 則報錯(Uncaught (in promise) AggregateError: All promises were rejected)
3. AggregateError
a new Error type to represent multiple errors at once (一個新的 Error type, 把多個 Errors 包在一起)
Promise.any([Promise.reject("error1"), Promise.reject("error2"), Promise.reject("error3")]).catch((err) => err);
/*
AggregateError{
errors: (3) ['error1', 'error2', 'error3']
message: "All promises were rejected"
stack: "AggregateError: All promises were rejected"
}
*/
4. ??=, &&=, ||=
let a = undefined;
let b = 1;
a ??= b; // 如果a是nullish(null, undefined), 將b賦值到a
let a = 1;
a &&= 10; // 如果a是truthy,則賦值到a (a = 10)
let b = 0;
b &&= 10; // 如果b是falsy,則不賦值 (b = 0)
let a = 1;
a ||= 10; // 如果a是truthy,則不賦值 (a = 0)
let b = 0;
b ||= 10; // 如果b是falsy,則賦值到b (b = 10)
5. WeakRef
for referring to a target object without preserving it from garbage collection
6. FinalizationRegistry
to manage registration and unregistration of cleanup operations performed when target objects are garbage collected (在註冊的物件被回收時,執行 callback)
const r = new FinalizationRegistry(
() => console.log("callback")
);
(() => {
let obj = { a: 1, b: 2 }
r.register(obj)
})();